The Importance of Floodplains
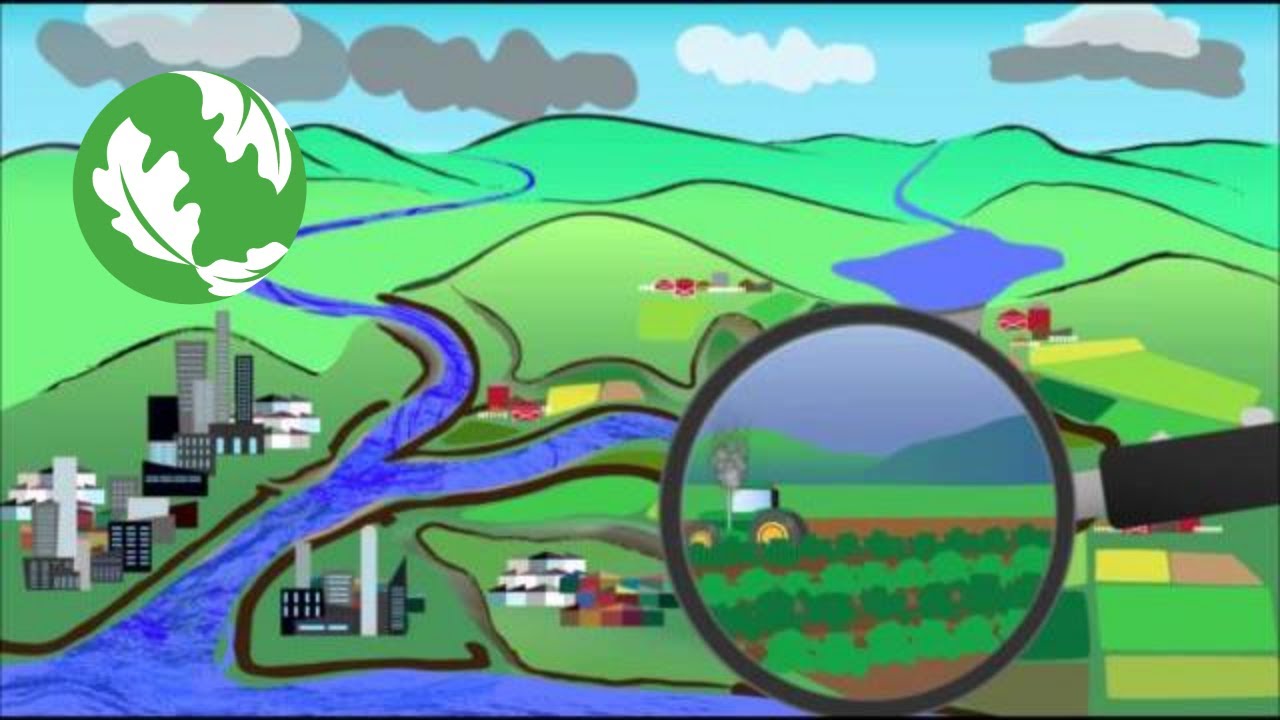
Floodplains play a crucial role in the natural environment and in the lives of communities living near water bodies. These low-lying areas adjacent to rivers, streams, and other bodies of water serve as a vital component in managing flood risks and supporting biodiversity.
Functions of Floodplains
Flood Mitigation: Floodplains act as natural buffers during heavy rainfall or snowmelt, absorbing excess water and reducing the impact of flooding on surrounding areas.
Biodiversity: These areas provide habitats for diverse plant and animal species, contributing to ecological balance and supporting wildlife populations.
Water Quality: Floodplains help filter pollutants from water sources, improving water quality for both human consumption and ecosystem health.
Challenges and Conservation Efforts
Despite their importance, floodplains face threats from urban development, deforestation, and climate change. Encroachment on these sensitive ecosystems can lead to increased flood risks and loss of biodiversity.
To address these challenges, conservation efforts focus on preserving and restoring natural floodplain functions. Strategies include land-use planning, wetland restoration, and community engagement to promote sustainable practices near flood-prone areas.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recognizing the value of floodplains is essential for sustainable water management and disaster risk reduction. By safeguarding these critical ecosystems, we can enhance resilience to floods, protect biodiversity, and promote the well-being of both nature and communities.
Benefits of Floodplains: Nature’s Flood Buffers and Biodiversity Havens
- Natural flood buffers that reduce the impact of flooding on surrounding areas.
- Provide habitats for diverse plant and animal species, supporting biodiversity.
- Help filter pollutants from water sources, improving water quality.
- Support agricultural activities by replenishing soil nutrients through periodic flooding.
- Offer recreational opportunities such as fishing, birdwatching, and nature trails.
- Serve as valuable educational resources for studying ecosystems and hydrology.
6 Drawbacks of Floodplains: Risks to Communities, Agriculture, Infrastructure, and the Environment
- Increased flood risk to nearby communities during heavy rainfall.
- Loss of agricultural land due to periodic flooding in floodplain areas.
- Potential damage to infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and buildings from floodwaters.
- Contamination of water sources with pollutants carried by floodwaters.
- Disruption of ecosystems and loss of biodiversity from altered flow patterns in floodplains.
- Higher insurance costs for properties located in floodplain zones.
Natural flood buffers that reduce the impact of flooding on surrounding areas.
One significant advantage of floodplains is their role as natural flood buffers, effectively reducing the impact of flooding on nearby areas. By absorbing excess water during heavy rainfall or snowmelt, floodplains help mitigate flood risks and minimize potential damage to surrounding communities. This vital function not only protects human settlements and infrastructure but also contributes to overall flood resilience by providing a natural barrier that can absorb and disperse floodwaters, ultimately safeguarding lives and properties in flood-prone regions.
Provide habitats for diverse plant and animal species, supporting biodiversity.
Floodplains serve as valuable habitats for a wide range of plant and animal species, contributing significantly to biodiversity conservation. The diverse vegetation and unique environmental conditions found in floodplains support various wildlife populations, including birds, fish, amphibians, and insects. By providing a rich and interconnected ecosystem, floodplains play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and preserving the genetic diversity of species. Protecting these habitats is essential for sustaining healthy ecosystems and ensuring the survival of numerous plant and animal species that rely on floodplains for their survival.
Help filter pollutants from water sources, improving water quality.
Floodplains serve a crucial role in improving water quality by acting as natural filters that help remove pollutants from water sources. As floodwaters flow through these low-lying areas, sediments and contaminants are trapped and absorbed, preventing them from reaching rivers, lakes, and other bodies of water. This process not only enhances the quality of drinking water but also supports the health of aquatic ecosystems by reducing the impact of harmful substances. By serving as effective filtration systems, floodplains play a vital role in maintaining clean and healthy water resources for both human consumption and environmental sustainability.
Support agricultural activities by replenishing soil nutrients through periodic flooding.
Floodplains provide a valuable benefit to agricultural activities by replenishing soil nutrients through periodic flooding. When floodwaters overflow onto these low-lying areas, they deposit nutrient-rich sediments that enhance the fertility of the soil. This natural process helps sustain agricultural productivity by supplying essential nutrients that promote the growth of crops. Farmers can take advantage of this natural replenishment cycle to maintain healthy soil quality and improve crop yields, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices in floodplain regions.
Offer recreational opportunities such as fishing, birdwatching, and nature trails.
Floodplains provide valuable recreational opportunities for outdoor enthusiasts, offering activities such as fishing, birdwatching, and nature trails. These natural settings not only allow individuals to connect with the environment but also promote physical activity and relaxation. Fishing enthusiasts can enjoy casting their lines in the calm waters of floodplains, while birdwatchers can observe a variety of avian species in their natural habitats. Additionally, nature trails winding through floodplain areas provide a serene setting for hiking, cycling, and exploring the diverse flora and fauna that thrive in these ecosystems. Overall, floodplains serve as versatile recreational spaces that cater to a wide range of interests and foster a deeper appreciation for nature’s beauty.
Serve as valuable educational resources for studying ecosystems and hydrology.
Floodplains serve as valuable educational resources for studying ecosystems and hydrology. These dynamic areas provide a real-world laboratory for researchers, students, and environmental enthusiasts to observe the interactions between water flow, vegetation, wildlife, and geological features. By studying floodplains, individuals can gain insights into the complex relationships within ecosystems and hydrological processes, enhancing our understanding of how natural systems function and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Increased flood risk to nearby communities during heavy rainfall.
One significant drawback of floodplains is the increased flood risk they pose to nearby communities during periods of heavy rainfall. While floodplains naturally absorb excess water and help mitigate flooding to some extent, intense precipitation events can overwhelm these areas, leading to water overflow and potential inundation of surrounding neighborhoods. This heightened flood risk can result in property damage, displacement of residents, and disruption of daily life for those living in close proximity to floodplains. Efforts to manage this con often involve implementing effective floodplain management strategies, such as zoning regulations, levee construction, and community awareness programs to minimize the impact of floods on vulnerable populations.
Loss of agricultural land due to periodic flooding in floodplain areas.
The loss of agricultural land due to periodic flooding in floodplain areas poses a significant challenge for farmers and food production. When floodwaters inundate farmland, crops are destroyed, soil fertility is compromised, and infrastructure is damaged, leading to economic losses and food security concerns. The recurrent nature of flooding in floodplains can disrupt agricultural activities, hinder crop yields, and impact the livelihoods of those dependent on farming in these vulnerable regions. Efforts to mitigate the impact of flooding on agricultural land in floodplains require strategic planning, sustainable land management practices, and innovative solutions to support farmers and ensure food production resilience in the face of natural disasters.
Potential damage to infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and buildings from floodwaters.
One significant drawback of floodplains is the potential damage they pose to infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings when inundated by floodwaters. The destructive force of flooding can weaken structures, wash away roads, and compromise the stability of bridges, leading to costly repairs and disruptions to transportation networks. This threat highlights the importance of careful planning and mitigation measures to minimize the impact of floods on critical infrastructure located in flood-prone areas.
Contamination of water sources with pollutants carried by floodwaters.
One significant drawback of floodplains is the potential contamination of water sources with pollutants carried by floodwaters. When floods occur, these low-lying areas can act as conduits for various pollutants such as chemicals, sewage, and debris to be transported into rivers, lakes, and groundwater reservoirs. This contamination poses a serious threat to water quality, impacting both human health and ecosystem integrity. Efforts to mitigate this con of floodplains include implementing effective pollution control measures, promoting sustainable land use practices, and enhancing monitoring systems to safeguard water sources from the harmful effects of flood-induced pollutants.
Disruption of ecosystems and loss of biodiversity from altered flow patterns in floodplains.
The disruption of ecosystems and loss of biodiversity due to altered flow patterns in floodplains pose a significant con that warrants attention. Changes in water flow, whether from human alterations or natural events, can disturb the delicate balance of flora and fauna that depend on the regular flooding cycles of these areas. Such disruptions can lead to habitat degradation, loss of species diversity, and ultimately impact the overall health and resilience of the ecosystem. Conservation efforts are crucial to mitigate these negative effects and preserve the unique biodiversity supported by floodplains.
Higher insurance costs for properties located in floodplain zones.
Properties located in floodplain zones often face the con of higher insurance costs due to the elevated risk of flooding. Insurance companies typically charge higher premiums for properties in these areas to offset the increased likelihood of flood damage. This financial burden can be a significant concern for property owners, as it adds to the overall cost of homeownership and may impact affordability. The higher insurance costs associated with floodplain properties highlight the importance of understanding and managing flood risks effectively to mitigate financial implications for homeowners and promote resilient communities.