The Impact of Floods: Understanding the Devastating Consequences
Floods are natural disasters that can have catastrophic effects on communities, infrastructure, and the environment. When heavy rainfall, storm surges, or rapid snowmelt exceed the capacity of water bodies to contain them, flooding occurs, leading to widespread damage and loss.
Immediate Effects of Floods
During a flood event, immediate consequences include:
- Destruction of homes and buildings
- Disruption of transportation networks
- Loss of crops and livestock
- Contamination of drinking water sources
- Displacement of communities
Long-Term Impacts
The aftermath of a flood can have lasting effects on a region:
- Economic losses due to property damage and business closures
- Increased risk of waterborne diseases and public health concerns
- Environmental degradation from pollution and habitat destruction
- Potential for social unrest and psychological trauma among affected populations
- Challenges in rebuilding infrastructure and restoring livelihoods
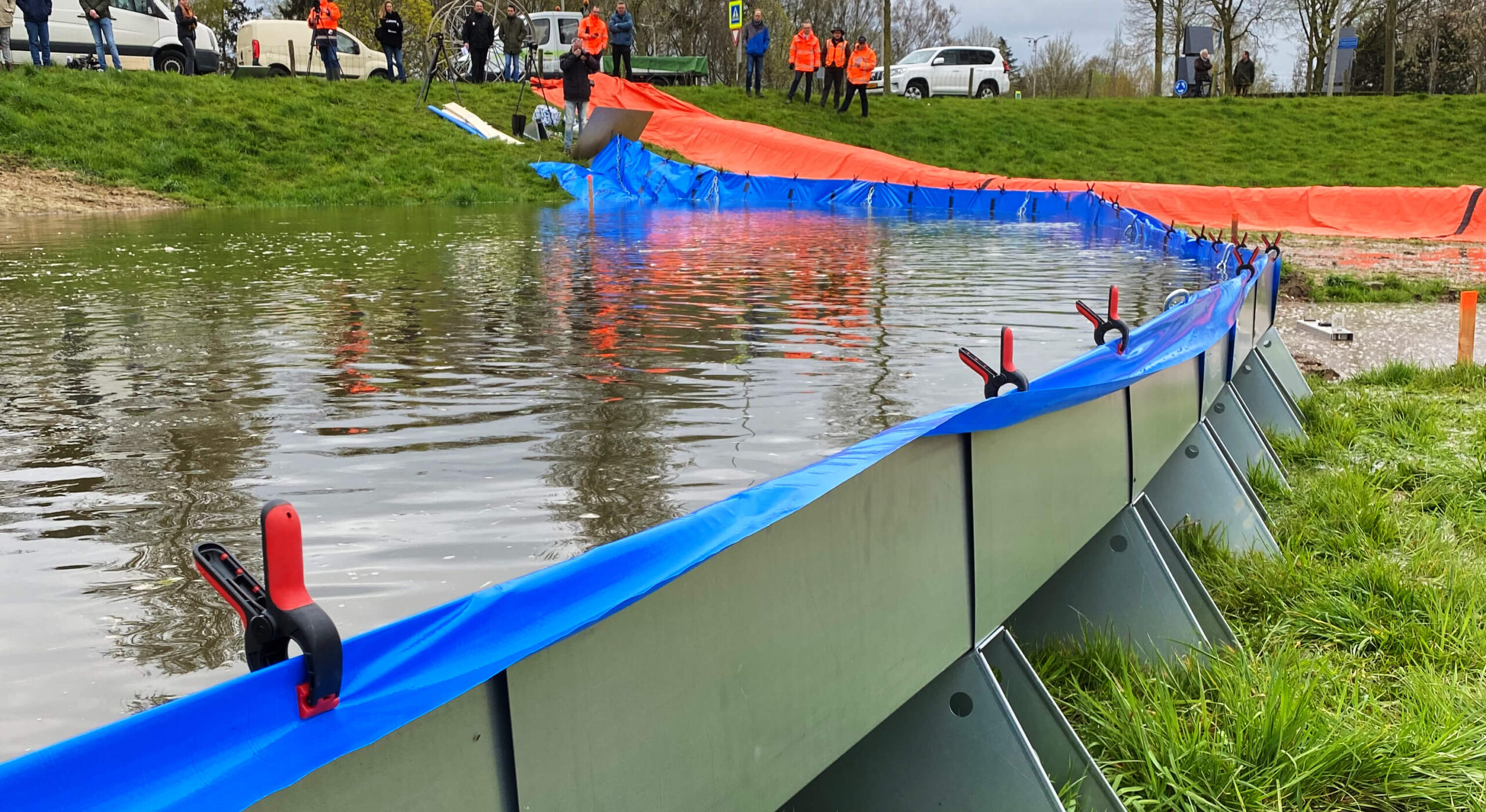
Flood Preparedness and Mitigation Strategies
To reduce the impact of floods, communities can implement various preparedness measures:
- Developing early warning systems to alert residents about impending floods
- Building resilient infrastructure that can withstand floodwaters
- Educating the public about evacuation routes and safety procedures during floods
- Promoting sustainable land use practices to reduce runoff and erosion risks
In conclusion, understanding the devastating consequences of floods is crucial for effective disaster management. By investing in preparedness efforts and adopting mitigation strategies, communities can minimize the impact of floods and enhance their resilience in the face of future disasters.
Understanding Floods: Causes, Historical Events, Definitions, and Current Inquiries
- What causes floods?
- What is the largest flood in history?
- What is this floods?
- What is the definition of a flood?
What causes floods?
Floods can be caused by various factors, including heavy rainfall, snowmelt, storm surges, and overflowing rivers or dams. When the amount of water entering a particular area exceeds the capacity of the land or water bodies to absorb it, flooding occurs. Urbanization and deforestation can also contribute to floods by reducing natural drainage systems and increasing runoff. Climate change is another significant factor that can intensify flooding events due to altered precipitation patterns and rising sea levels. Understanding the multiple causes of floods is essential for implementing effective mitigation strategies and enhancing community resilience against these natural disasters.
What is the largest flood in history?
The largest flood in recorded history is believed to be the Great Flood of 1931 in China. This devastating event occurred during the Yangtze River’s overflow, affecting millions of people and causing widespread destruction across the region. The floodwaters submerged entire cities, leading to a staggering loss of life and property. The Great Flood of 1931 serves as a sobering reminder of the destructive power of floods and highlights the importance of effective disaster preparedness and mitigation measures to minimize such catastrophic events in the future.
What is this floods?
Floods are natural disasters characterized by the overflow of water onto land that is typically dry. They occur when heavy rainfall, melting snow, or storm surges lead to an excess of water that cannot be absorbed by the soil or contained in rivers and lakes. Floods can cause significant damage to homes, infrastructure, and agriculture, posing risks to human life and safety. Understanding the causes and impacts of floods is essential for effective disaster preparedness and response efforts in vulnerable regions.
What is the definition of a flood?
A flood is defined as an overflow of water onto land that is typically dry, caused by heavy rainfall, snowmelt, storm surges, or the sudden release of water from a dam or levee. Floods can occur gradually over time or suddenly with little warning, leading to inundation of homes, roads, and other infrastructure. The extent and severity of a flood can vary widely, from localized flash floods to widespread riverine flooding that affects entire regions. Understanding the definition of a flood is essential for preparedness and response efforts to mitigate the impact of these natural disasters on communities and ecosystems.